You know that nutrients are essential constituents of food that must be supplied to the body in suitable amounts. There are around 40 essential nutrients that (based on their chemical structure and properties) are placed in five categories. There are carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Water has the unique status of food as well as that of a macronutrient.
Welcome To Odisha Regional Stuy Point
We Provide the best e preparation for all competitive exam In ଓଡ଼ିଆ Language…
Download Our Mobile App – ORSP EDUCATION
|THE MACRONUTRIENTS-I: CARBOHYDRATES AND WATER |
|DECE2 UNIT 4 Important Question|
|Exercise 1 Solution|
- What do we mean by the protein-sparing action of carbohydrates?
Ans-- Both proteins and carbohydrates can be broken down in the body to provide energy.
- The main function of carbohydrates is to furnish energy for the body; this is not the case with proteins. The presence of carbohydrates in the diet takes care of the energy needs of the body and hence spares proteins for their chief function of growth and body-building. This function of carbohydrates is termed protein-sparing action.
- Is it harmful to eat too little carbohydrates?
Ans-- Yes. Eating too little carbohydrates would force the body to break down large
- amounts of fat. This results in the accumulation of substances that are harmful.
|THE MACRONUTRIENTS-I: CARBOHYDRATES AND WATER |
|DECE2 UNIT 4 Important Question|
|Exercise 2 Solution|
- What are simple sugars?
Ans-
Glucose, fructose and galactose are simple sugars. - Fill in the blanks.
a) The principal site of carbohydrate digestion is the ……………………………….
b) ………………… and …………………are the major sources of carbohydrates in our diets.
C) One gram of carbohydrate provides approximately …………………… Kcal.
d) ……………………… is the storage form of glucose in the body.
Ans-
a) Small intestine
b) Cereals and sugars
c) 4 Kcal
d) Glycogen
|THE MACRONUTRIENTS-I: CARBOHYDRATES AND WATER |
|DECE2 UNIT 4 Important Question|
|Exercise 3 Solution|
- What is the role of fiber in relieving constipation?
Ans-
The dietary fiber present in food cannot be digested in the body.
The unabsorbed food residue chiefly containing indigestible fiber absorbs water, gives bulk to the stools, and helps in their easy elimination from the body. Thus, fiber plays a role in relieving constipation - Fill in the blanks.
a) …………………………… and ……………………… are termed refined cereals .
b) Fibre is the term used for ………………………………… carbohydrates such as ………………………..
c) ………………………………… and ……………………… are some of the rich sources of fiber.
Ans-
a) Maida and suji
b) non-available, cellulose
c) whole cereals and pulses
|THE MACRONUTRIENTS-I: CARBOHYDRATES AND WATER |
|DECE2 UNIT 4 Important Question|
|Exercise 4 Solution|
- What is the meaning of the term ‘water balance?’
Ans-
Intake of water into the body from all three sources (i.e. water as such and in the form of beverages, water from foods, water produced in the body from the metabolism of nutrients) is termed ingestion. Some amount of water is lost from the body during the course of its utilization. This is termed excretion of water. Usually, in normal conditions, the body maintains a balance between ingestion of water and excretion of water. This is termed water balance. - Fill in the blanks.
a) Our normal body temperature is …………………………………………………..
b) Water makes up approximately …………………………… percent of the total weight of an adult.
Ans-
a) 98.4oF or 37oC
b) 60 – 70 percent.
|THE MACRONUTRIENTS-I: CARBOHYDRATES AND WATER |
|DECE2 UNIT 4 Important Question|
|Extra Important Question|
Q1. Describe the processes of digestion, absorption and utilization of food.(10 MARK)
भोजन के पाचन, अवशोषण और उपयोग की प्रक्रियाओं का वर्णन करें
Digestion of Food:
Let us now take a look at the overall process of how digestion occurs. Digestion takes place step-by-step at various sites in the digestive tract .
भोजन का पाचन:
आइए अब पाचन कैसे होता है, इसकी समग्र प्रक्रिया पर एक नजर डालते हैं। पाचन तंत्र में विभिन्न स्थानों पर पाचन चरण-दर-चरण होता है।
Mouth:
- the process of digestion begins in the mouth where food is chewed by the teeth and mixed with saliva.
- While the food is still in the mouth, it is acted upon by an enzyme, which acts only on cooked carbohydrates such as starch and partially digests them or breaks them up into smaller units.
मुंह:
- पाचन की प्रक्रिया मुंह में शुरू होती है जहां भोजन को दांतों से चबाया जाता है और लार के साथ मिलाया जाता है।
- जबकि भोजन अभी भी मुंह में है, यह एक एंजाइम द्वारा कार्य करता है, जो केवल पके हुए कार्बोहाइड्रेट जैसे स्टार्च पर कार्य करता है और आंशिक रूप से उन्हें पचाता है या उन्हें छोटी इकाइयों में तोड़ देता है।

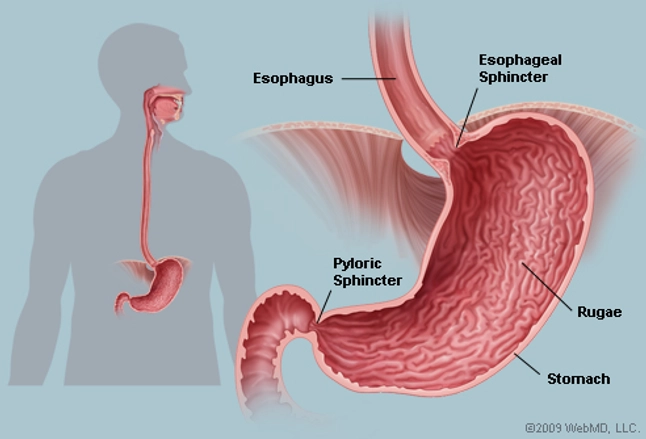
Stomach:
- The chewed food mixed with saliva then passes into the stomach through the tube-like structure called the esophagus.
- Here it gets mixed with the digestive juice present in the stomach called gastric juice which is acidic in nature.
- Mixing of food with the gastric juice converts the food into a thin soup-like consistency.
- Gastric juice contains an enzyme which acts on proteins and brings about their partial digestion. Other nutrients in food remain chemically unchanged.
पेट:
- चबाया हुआ भोजन लार के साथ मिश्रित होकर फिर नली जैसी संरचना के माध्यम से पेट में जाता है जिसे अन्नप्रणाली कहा जाता है।
- यहाँ यह पेट में मौजूद पाचक रस के साथ मिल जाता है जिसे जठर रस कहते हैं जो कि अम्लीय प्रकृति का होता है।
- भोजन को जठर रस के साथ मिलाने से भोजन एक पतले सूप जैसी स्थिरता में परिवर्तित हो जाता है।
- गैस्ट्रिक जूस में एक एंजाइम होता है जो प्रोटीन पर कार्य करता है और उनका आंशिक पाचन करता है। भोजन में अन्य पोषक तत्व रासायनिक रूप से अपरिवर्तित रहते हैं।
Small intestine:
- The next stop in the digestive tract is the small intestine.
- The partially digested mass of food passes from the stomach into the small intestine.
- The small intestine not only contains intestinal juice (which is secreted from the small intestine itself) but also secretions from the liver and pancreas.
- The secretion from the liver is called bile and from the pancreas is known as pancreatic juice.
- Bile aids in the digestion and absorption of fats (you will learn about the role of bile in fat digestion in the next Unit).
- Both pancreatic and intestinal juices contain enzymes which break down fats, proteins and carbohydrates into simpler substances.
- These simple substances ultimately reach the bloodstream.
छोटी आंत:
- पाचन तंत्र में अगला पड़ाव छोटी आंत है।
- भोजन का आंशिक रूप से पचा हुआ द्रव्यमान पेट से छोटी आंत में जाता है।
- छोटी आंत में न केवल आंतों का रस होता है (जो छोटी आंत से ही स्रावित होता है) बल्कि यकृत और अग्न्याशय से भी स्राव होता है।
- जिगर से स्राव को पित्त कहा जाता है और अग्न्याशय से अग्नाशयी रस के रूप में जाना जाता है।
- पित्त वसा के पाचन और अवशोषण में सहायक होता है (आप अगली इकाई में वसा के पाचन में पित्त की भूमिका के बारे में जानेंगे)।
- अग्न्याशय और आंतों के रस दोनों में एंजाइम होते हैं जो वसा, प्रोटीन और कार्बोहाइड्रेट को सरल पदार्थों में तोड़ते हैं।
- ये सरल पदार्थ अंततः रक्तप्रवाह में पहुंच जाते हैं।
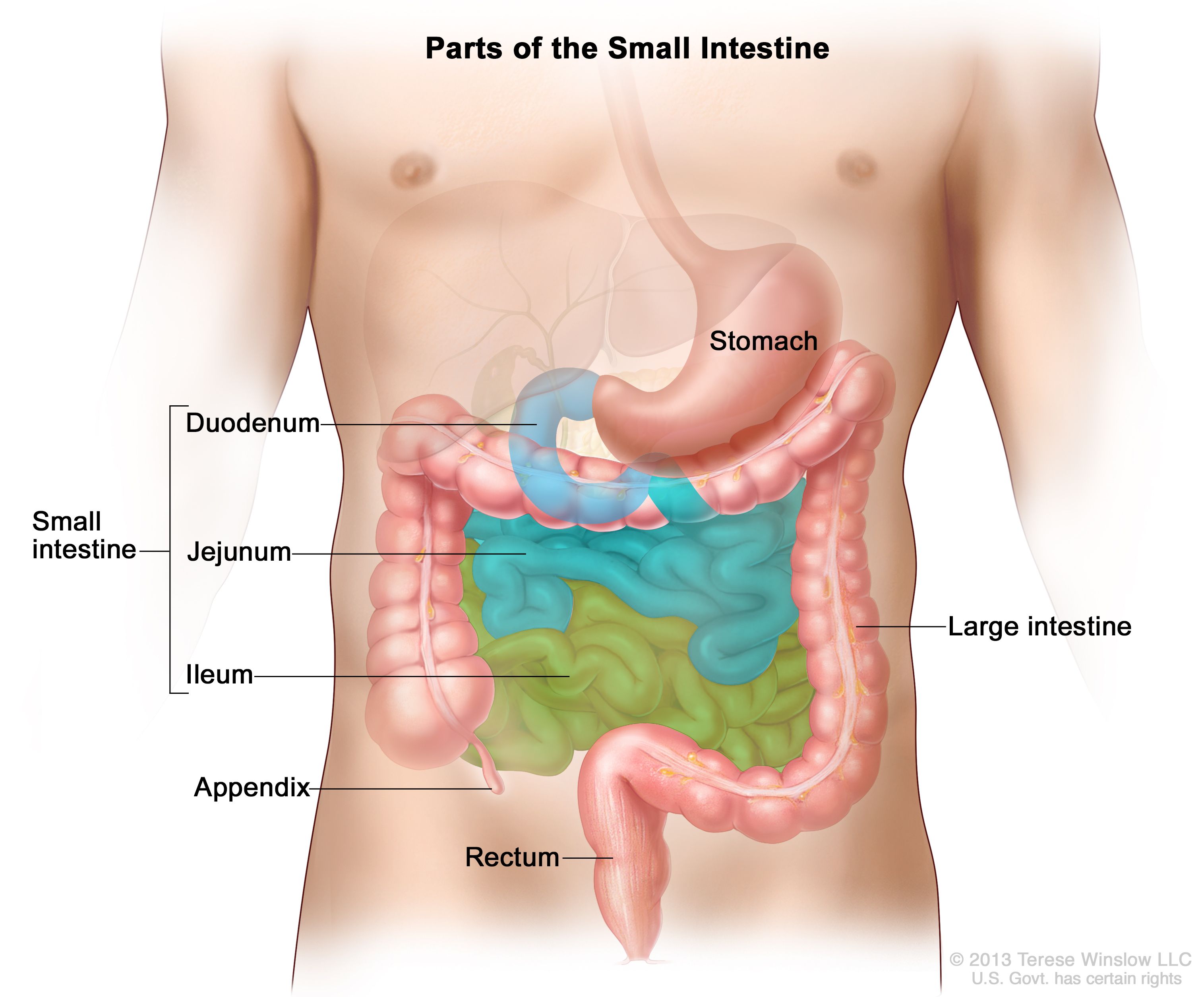
Large intestine:
- The components of food which are not absorbed in the small intestine along with a large amount of water passes on to the large intestine.
- Here, most of the excess water is reabsorbed and the remaining water and solid matter is eliminated from the body.
बड़ी आंत:
- भोजन के वे घटक जो बड़ी मात्रा में पानी के साथ छोटी आंत में अवशोषित नहीं होते हैं, बड़ी आंत में चले जाते हैं।
- यहां, अधिकांश अतिरिक्त पानी पुन: अवशोषित हो जाता है और शेष पानी और ठोस पदार्थ शरीर से समाप्त हो जाते हैं।

Absorption of Food:
- Absorption takes place in the small intestine.
- The end products of digestion or the nutrients present in the small intestine can be used by the body only when they enter the bloodstream.
- This process of movement of digested food or nutrients across the intestinal wall to the bloodstream is termed absorption of food.
- The wall of the small intestine is made up of numerous folds or finger-like projections known as villi.
- The presence of these villi tremendously increase the total area from which absorption can take place.
- Most of the nutrients are absorbed from the upper part of the small intestine though some are absorbed from the lower portion.
भोजन का अवशोषण:
- अवशोषण छोटी आंत में होता है।
- पाचन के अंतिम उत्पाद या छोटी आंत में मौजूद पोषक तत्व शरीर द्वारा तभी उपयोग किए जा सकते हैं जब वे रक्तप्रवाह में प्रवेश करते हैं।
- पचे हुए भोजन या पोषक तत्वों को आंतों की दीवार से रक्तप्रवाह में ले जाने की इस प्रक्रिया को भोजन का अवशोषण कहा जाता है।
- छोटी आंत की दीवार विली के नाम से जानी जाने वाली कई सिलवटों या उंगली जैसे प्रोजेक्शन से बनी होती है।
- इन विली की उपस्थिति से उस कुल क्षेत्रफल में अत्यधिक वृद्धि होती है जिससे अवशोषण हो सकता है।
- अधिकांश पोषक तत्व छोटी आंत के ऊपरी हिस्से से अवशोषित होते हैं, हालांकि कुछ निचले हिस्से से अवशोषित होते हैं।

As you know, the end products of digestion move into the bloodstream. The blood circulating in the body and therefore, the nutrients it carries reaches every cell of the body. Once they reach the cell, the nutrients perform their specific functions.
जैसा कि आप जानते हैं, पाचन के अंतिम उत्पाद रक्तप्रवाह में चले जाते हैं। शरीर में रक्त का संचार होता है और इसलिए इसके द्वारा वहन किए जाने वाले पोषक तत्व शरीर की हर कोशिका तक पहुँचते हैं। एक बार जब वे कोशिका में पहुँच जाते हैं, तो पोषक तत्व अपने विशिष्ट कार्य करते हैं।
Utilization of Food:
- In order to be utilized for specific functions the absorbed end products or the nutrients from the food we eat further undergo chemical changes.
- They are either further broken down to release energy or are used to -form more complex substances.
- Metabolism is a general term. It refers to all the chemical changes that take place in the cells after the end products of digestion are absorbed.
- It is of two types breakdown of complex substances into simpler ones and manufacture of complex substances from simple ones.
भोजन का उपयोग:
- विशिष्ट कार्यों के लिए उपयोग किए जाने के लिए अवशोषित अंत उत्पादों या भोजन से पोषक तत्व जो हम खाते हैं, रासायनिक परिवर्तनों से गुजरते हैं।
- वे या तो ऊर्जा मुक्त करने के लिए टूट जाते हैं या अधिक जटिल पदार्थों को बनाने के लिए उपयोग किए जाते हैं।
- चयापचय एक सामान्य शब्द है। यह उन सभी रासायनिक परिवर्तनों को संदर्भित करता है जो पाचन के अंतिम उत्पादों के अवशोषित होने के बाद कोशिकाओं में होते हैं।
- यह दो प्रकार का होता है जटिल पदार्थों का सरल पदार्थों में टूटना और सरल पदार्थों से जटिल पदार्थों का निर्माण।
Q5. Distinguish between available and non-available carbohydrates.(5 MARK)
Carbohydrates are a combination of oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon that are packed into starch, sugar or fibre. Carbohydrates are of two types, available and non-available.
Explanation:
Available carbohydrates are starch and sugar that are energy sources for the body. They are broken down into glucose and utilized by the body in different bio-chemical reactions.
Non-available ‘carbohydrates are not digested’ and absorbed by the body. They are fibres that are helpful for the ‘body to digest’ other foods, bowel movement and for prevention against certain diseases.
उपलब्ध और गैर-उपलब्ध कार्बोहाइड्रेट के बीच भेद करें।
कार्बोहाइड्रेट ऑक्सीजन, हाइड्रोजन और कार्बन का एक संयोजन है जो स्टार्च, चीनी या फाइबर में पैक किया जाता है। कार्बोहाइड्रेट दो प्रकार के होते हैं, उपलब्ध और गैर-उपलब्ध।
स्पष्टीकरण:
उपलब्ध कार्बोहाइड्रेट स्टार्च और चीनी हैं जो शरीर के लिए ऊर्जा के स्रोत हैं। वे ग्लूकोज में टूट जाते हैं और शरीर द्वारा विभिन्न जैव-रासायनिक प्रतिक्रियाओं में उपयोग किया जाता है।
गैर-उपलब्ध ‘कार्बोहाइड्रेट पचता नहीं है’ और शरीर द्वारा अवशोषित किया जाता है। वे फाइबर हैं जो अन्य खाद्य पदार्थों को ‘पचाने’, मल त्याग और कुछ बीमारियों से बचाव के लिए सहायक होते हैं।
Q6. Describe the processes of digestion, absorption and utilization of carbohydrates in the body.
शरीर में कार्बोहाइड्रेट के पाचन, अवशोषण और उपयोग की प्रक्रियाओं का वर्णन करें
Carbohydrates are widely distributed in plant foods. They are mainly present in these foods in the form of three types of compounds called sugars, starches and fiber.
Carbohydrates are a combination of oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon that are packed into starch, sugar or fibre. Carbohydrates are of two types, available and non-available.
Available carbohydrates are starch and sugar that are energy sources for the body. They are broken down into glucose and utilized by the body in different bio-chemical reactions.
Non-available ‘carbohydrates are not digested’ and absorbed by the body. They are fibres that are helpful for the ‘body to digest’ other foods, bowel movement and for prevention against certain diseases.
पौधों के खाद्य पदार्थों में कार्बोहाइड्रेट व्यापक रूप से वितरित किए जाते हैं। वे मुख्य रूप से इन खाद्य पदार्थों में तीन प्रकार के यौगिकों के रूप में मौजूद होते हैं जिन्हें शर्करा, स्टार्च और फाइबर कहा जाता है।
कार्बोहाइड्रेट ऑक्सीजन, हाइड्रोजन और कार्बन का एक संयोजन है जो स्टार्च, चीनी या फाइबर में पैक किया जाता है। कार्बोहाइड्रेट दो प्रकार के होते हैं, उपलब्ध और गैर-उपलब्ध।
कार्बोहाइड्रेट ऑक्सीजन, हाइड्रोजन और कार्बन का एक संयोजन है जो स्टार्च, चीनी या फाइबर में पैक किया जाता है। कार्बोहाइड्रेट दो प्रकार के होते हैं, उपलब्ध और गैर-उपलब्ध।
उपलब्ध कार्बोहाइड्रेट स्टार्च और चीनी हैं जो शरीर के लिए ऊर्जा के स्रोत हैं। वे ग्लूकोज में टूट जाते हैं और शरीर द्वारा विभिन्न जैव-रासायनिक प्रतिक्रियाओं में उपयोग किया जाता है।
गैर-उपलब्ध ‘कार्बोहाइड्रेट पचता नहीं है’ और शरीर द्वारा अवशोषित किया जाता है। वे फाइबर हैं जो अन्य खाद्य पदार्थों को ‘पचाने’, मल त्याग और कुछ बीमारियों से बचाव के लिए सहायक होते हैं।
Welcome To Odisha Regional Stuy Point
We Provide the best e preparation for all competitive exam In ଓଡ଼ିଆ Language…
Download Our Mobile App – ORSP EDUCATION
